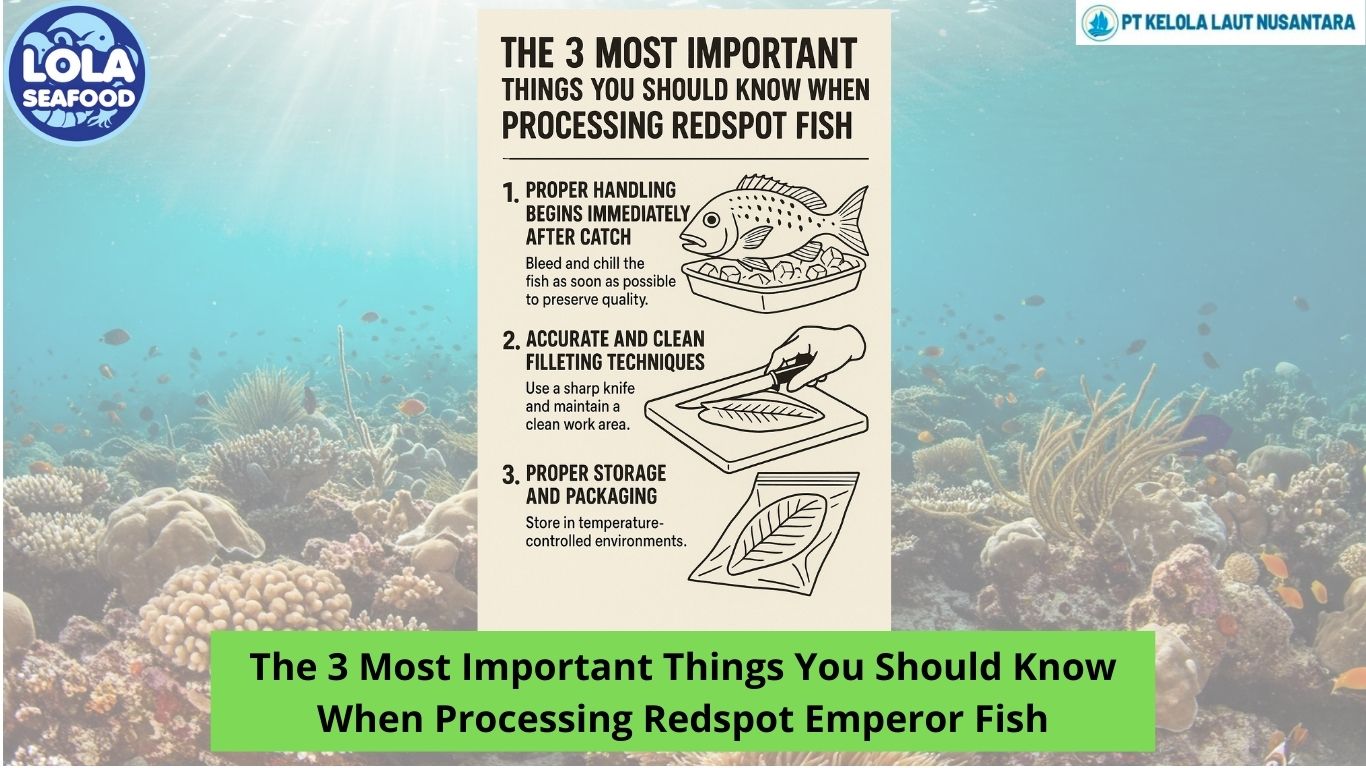
This Is What You Should Know About Crabs
By. Sofie Thoriq - 16 Dec 2024.jpg)
kelolalaut.com Crabs are fascinating crustaceans belonging to the order Decapoda, known for their distinctive hard exoskeletons and characteristic sideways walking. They are found in various environments, including oceans, freshwater bodies, and even on land. With over 6,800 species, crabs are incredibly diverse, ranging from tiny pea crabs to the giant Japanese spider crab, whose leg span can exceed 12 feet.
Anatomy and Behavior
Crabs have a compact, flattened body covered by a carapace and a pair of strong claws (chelae) used for defense, communication, and food handling. They are equipped with ten legs, with the last pair often modified for swimming or digging, depending on the species. Their eyes are located on stalks, providing a wide field of vision, essential for spotting predators and prey.
Habitat and Diet
Crabs inhabit diverse ecosystems, from coral reefs and mangroves to deep-sea floors and sandy beaches. Some, like the coconut crab, live entirely on land but return to the sea to reproduce. Crabs are omnivores, feeding on algae, plankton, mollusks, and organic debris, making them vital for nutrient recycling in their ecosystems.
Reproduction
Crabs have a unique reproductive process, with females often carrying fertilized eggs under their abdomen until they hatch into free-swimming larvae. These larvae undergo several molts before maturing into adult crabs.
Ecological and Economic Importance
Crabs play a critical role in maintaining the health of marine and coastal ecosystems. They contribute to the food chain as both predators and prey. Economically, crabs are a major seafood commodity. Species like the blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) and king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) are highly valued in global fisheries, generating significant revenue.
Here’s a detailed look at the nutrition facts for crab meat (based on a 3-ounce or 85-gram serving of cooked crab):
Nutrition Breakdown
|
Amount per 3 oz (85 g) |
% Daily Value (DV) |
|
|
Calories |
98 |
5% |
|
Protein |
20 g |
40% |
|
Total Fat |
1.3 g |
2% |
|
Saturated Fat |
0.3 g |
2% |
|
Cholesterol |
78 mg |
26% |
|
Carbohydrates |
0 g |
0% |
|
Fiber |
0 g |
0% |
|
Sugars |
0 g |
0% |
|
Sodium |
911 mg |
38% |
|
Omega-3 Fatty Acids |
~0.4 g |
--- |
Key Vitamins and Minerals
|
Nutrient |
Amount per 3 oz (85 g) |
% Daily Value (DV) |
|
Vitamin B12 |
9.8 mcg |
163% |
|
Zinc |
6.5 mg |
59% |
|
Copper |
0.9 mg |
100% |
|
Selenium |
36.4 mcg |
66% |
|
Phosphorus |
230 mg |
23% |
|
Folate |
51 mcg |
13% |
|
Magnesium |
53 mg |
13% |
Health Benefits of Crab
- High-Quality Protein: Crab provides lean protein essential for muscle growth and repair.
- Rich in Omega-3s: Beneficial for heart health, brain function, and reducing inflammation.
- Packed with Minerals: High levels of zinc, copper, and selenium support immune function, bone health, and thyroid regulation.
- Low in Calories and Fat: Great for those seeking a healthy, low-fat protein source.
Considerations
- Sodium Content: Crab is naturally high in sodium, so it may not be ideal for people on low-sodium diets.
- Cholesterol: While crab contains dietary cholesterol, its overall fat content is low, making it heart-friendly for most people.
If youre interested in our Cuttlefish Whole Round, Sweetlips Fillet Skinless, Indian Mackerel Whole Round please do not hesitate to contact us through email and/or whatsapp.

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)