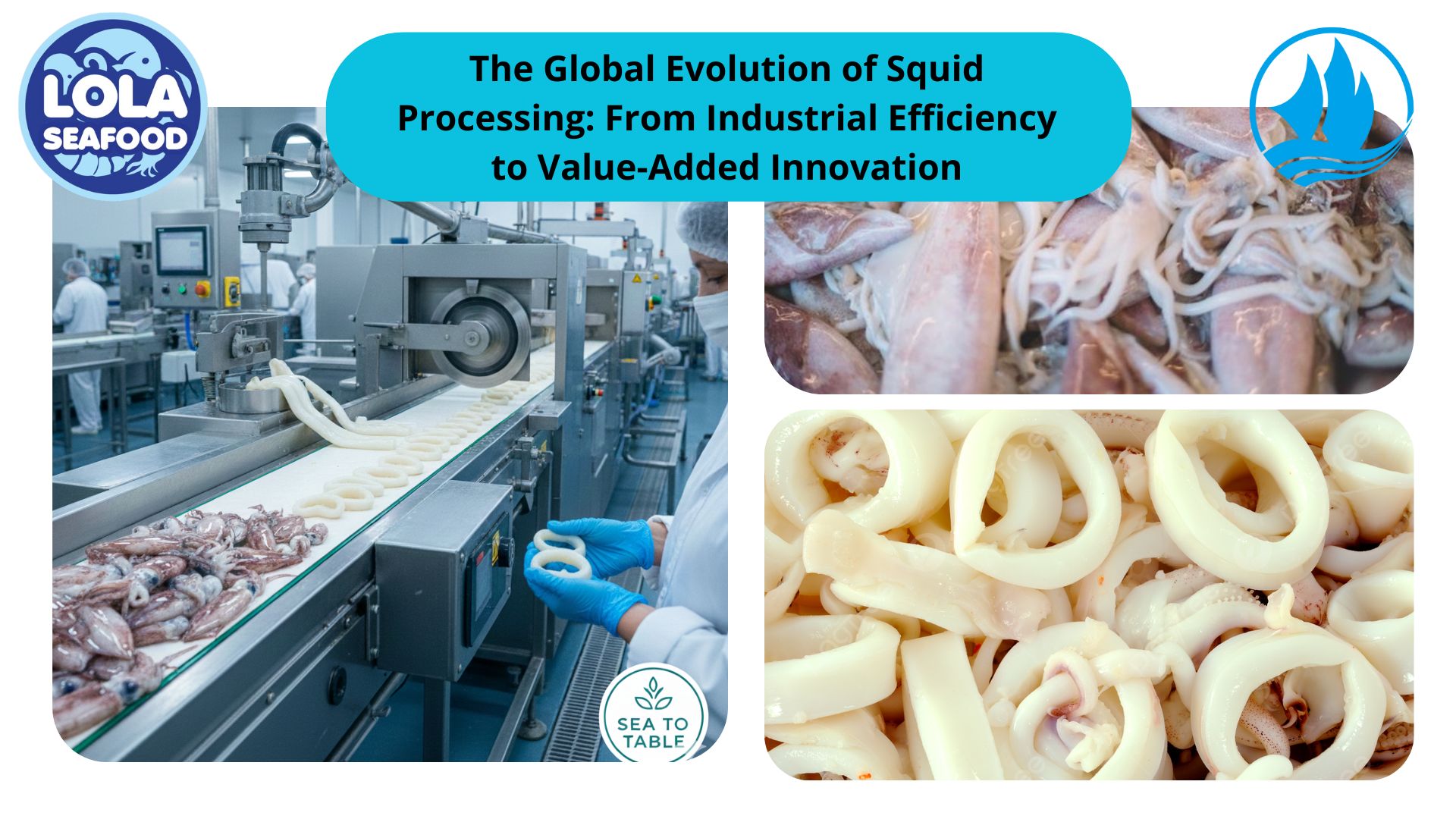
Here Are The Definition of Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
By. Lutfi - 10 Jan 2025 (1).png)
kelolalalut.com Economics is a science that studies how humans meet their needs with limited resources. In economics, there are two main branches with different focuses, namely microeconomics and macroeconomics. Here is an explanation:
1. Microeconomics
Microeconomics is a branch of economics that focuses on analyzing the behavior of individuals, households, or companies in making decisions regarding limited resources. Microeconomics studies how markets work, including the interaction between supply and demand and the formation of prices for goods and services.
Topics Studied in Microeconomics:
- Theory of Demand and Supply: Analyzes how the price and quantity of goods are determined in the market.
- Elasticity: Measures the responsiveness of demand or supply to changes in price, income, or other factors.
- Production and Cost Theory: Examines how companies produce goods and services and determine production costs.
- Market Structure: Studies various types of markets, such as perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly, and monopsony.
Examples of Microeconomic Applications:
- Analyzing the impact of fuel price increases on community consumption.
- Studying consumer purchasing decisions based on price and preferences.
2. Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of the economy as a whole or in aggregate. Its focus is on major variables such as economic growth, inflation, unemployment, and a country’s economic policies.
Topics Studied in Macroeconomics:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Measures the total value of goods and services produced by a country in a specific period.
- Inflation: Analyzes the general increase in prices of goods and services and its impact on purchasing power.
- Unemployment: Studies the unemployment rate and the factors influencing it.
- Fiscal and Monetary Policy: Examines how governments and central banks manage the economy through budgets and money supply control.
Examples of Macroeconomic Applications:
- Analyzing the impact of central bank interest rate policies on economic growth.
- Studying the effect of fiscal policy on unemployment rates.
Key Differences Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
|
Aspect |
Microeconomics |
Macroeconomics |
|
Study Object |
Individuals, households, and companies |
National or global economy |
|
Focus |
Supply, demand, and prices in the market |
Economic growth, inflation, and unemployment |
|
Scale of Analysis |
Specific |
Aggregate |
|
Example Studies |
Prices of certain goods, production costs |
Monetary policy, unemployment rates |
Relationship Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Although microeconomics and macroeconomics have different focuses, they are interrelated. Changes in microeconomics, such as price changes of goods, can influence macroeconomic variables like inflation. Conversely, macroeconomic policies, such as interest rate reductions, can impact microeconomic decisions, such as increased investments by companies.
Conclusion
Microeconomics and macroeconomics are two complementary branches of economics. A deep understanding of both aspects is essential for policymakers, business actors, and the general public to make effective decisions in managing resources and creating economic welfare.
If youre interested in our Cuttlefish Whole Round, Cuttlefish Fillet, Cuttlefish Pineapple Cut, and Cuttlefish Whole Cleaned please do not hesitate to contact us through email and/or whatsapp.
.jpg)
The Impact of HACCP-Based Integrated Quality Management Programs on the Quality and Competitiveness of Fresh Demersal Fish Products
 and Employee Productivity on the Demersal Fish Processing Floor.jpg)
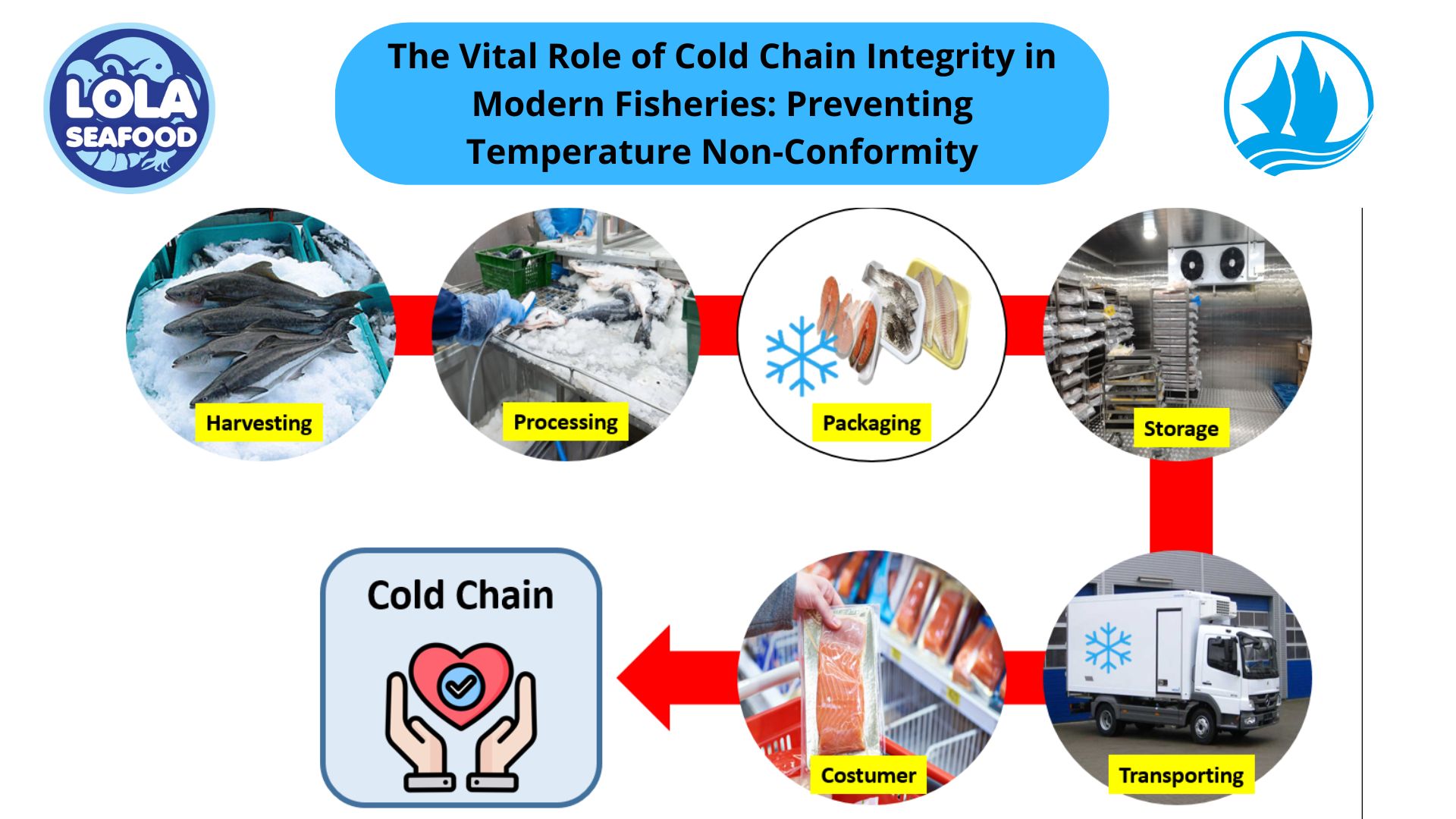
.jpg)