Here are the Definition of the Declining Balance Depreciation Method
By. Lutfi - 03 Feb 2025 (1).png)
kelolalaut.com The declining balance depreciation method is a fixed asset depreciation method that calculates depreciation as a fixed percentage of the asset’s book value each year. With this method, the depreciation expense is higher in the early years and gradually decreases over time. This method is suitable for assets that lose value more rapidly at the beginning of their use, such as vehicles, machinery, or technology equipment.
Formula for the Declining Balance Depreciation Method
Asset depreciation using the declining balance method is calculated using the following formula:
Depreciation for Year-n = Beginning Book Value×Depreciation Rate
Explanation:
- Beginning Book Value : The asset’s value at the start of the current year.
- Depreciation Rate : The percentage of depreciation determined based on company policy or accounting regulations.
In the double declining balance method, the depreciation rate is calculated as follows:
Depreciation Rate => 2x = (1 / Useful Life)
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Declining Balance Method
Advantages:
- Suitable for assets that depreciate quickly
This method more realistically reflects the value reduction of assets that experience faster depreciation in the early years.
- Lower tax burden in the early years
Since depreciation expenses are higher in the first few years, companies can reduce taxable income earlier.
- Better reflects the economic value of assets
Higher depreciation at the beginning aligns with the more intensive use of the asset in its early years.
Disadvantages:
- Uneven depreciation expenses
Since depreciation is higher in the early years and decreases over time, this method can make long-term budgeting more challenging.
- Does not reach a fixed residual value
In some cases, depreciation may never reach the predetermined residual value, requiring adjustments in the final year.
Example Calculation
Suppose a company purchases a machine for Rp 100,000,000 with a useful life of 5 years and applies the declining balance method with a 40% depreciation rate.
Year 1:
Depreciation = 100,000,000×40% = 40,000,000
Book value at the end of year 1 = 100,000,000 - 40,000,000 = Rp 60,000,000
Year 2:
Depreciation = 60,000,000×40% = 24,000,000
Book value at the end of year 2 = 60,000,000 - 24,000,000 = Rp 36,000,000
And so on, until the asset’s value reaches its residual amount.
Conclusion
The declining balance depreciation method is an effective way to reflect higher asset usage in the early years. Despite its disadvantages in long-term financial planning, this method remains a preferred choice for companies with assets that depreciate quickly.
If youre interested in our Cobia Whole Round / Whole Gilled Gutted please do not hesitate to contact us through email and/or whatsapp.

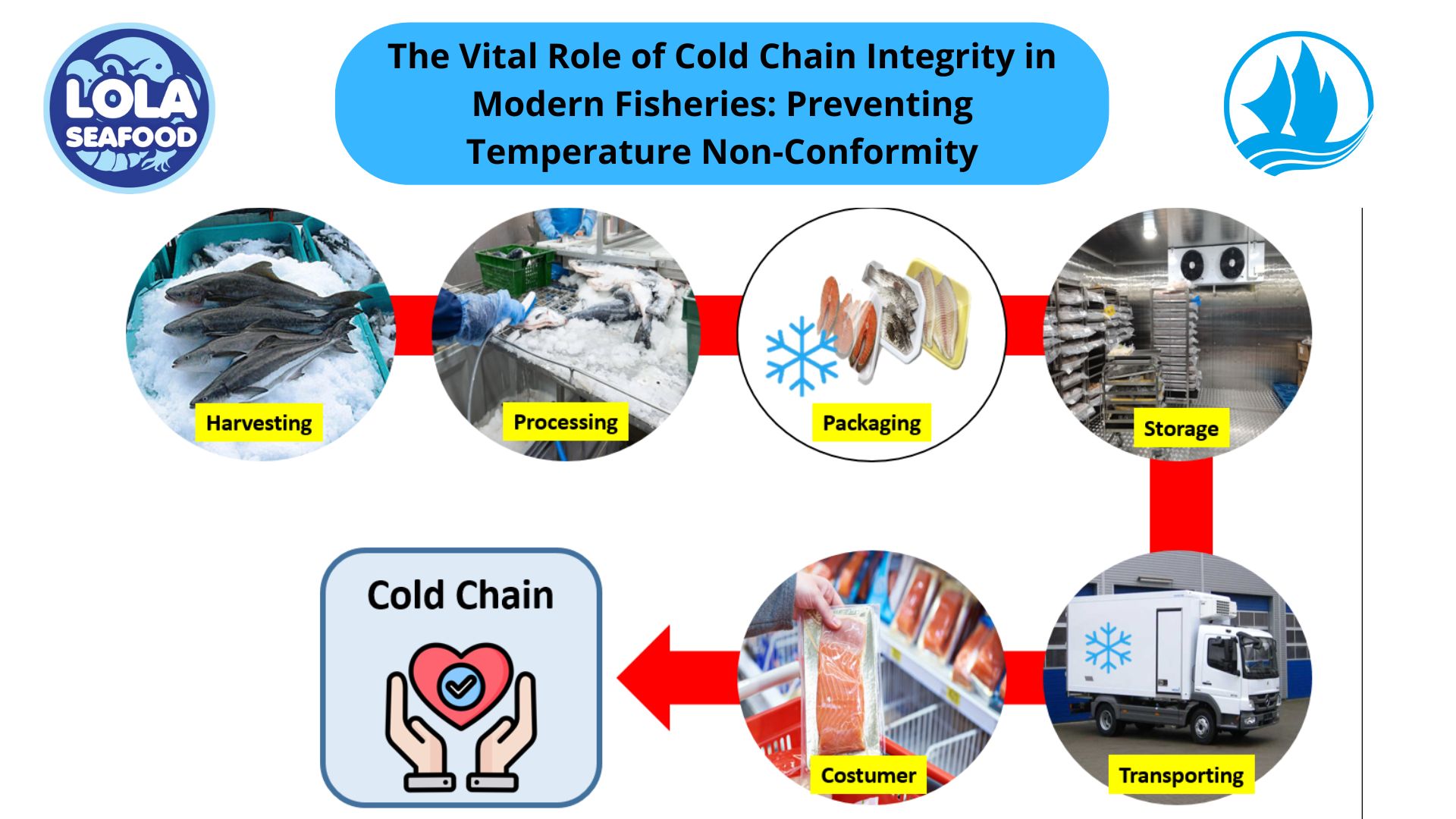
Optimizing Wild-Caught Fish Logistics: Maintaining Thermal Core Integrity During Long-Haul Transport
.jpg)


.jpg)
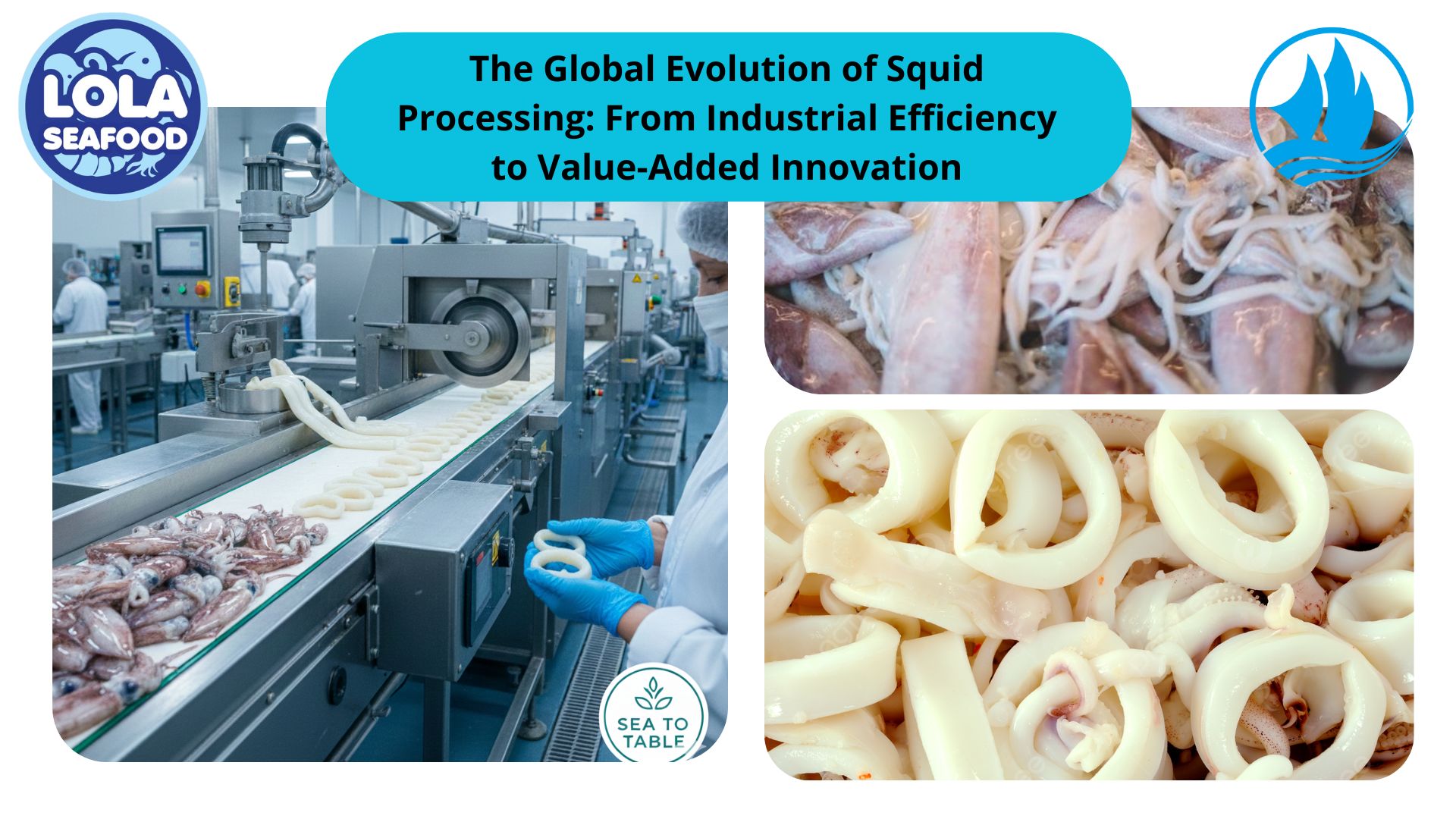
 and Employee Productivity on the Demersal Fish Processing Floor.jpg)
