The Crucial Ecological Roles of Sea Cucumbers
By. Nevanda - 22 Sep 2023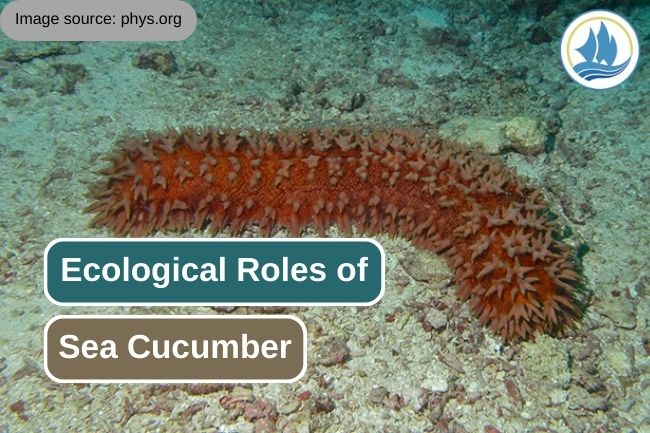
kelolalaut.com - Sea cucumbers play important ecological roles in marine ecosystems, contributing to the health and balance of these environments. Their ecological functions encompass various aspects of nutrient cycling, sediment stability, and biodiversity support. Here are some of the key ecological roles of sea cucumbers:
1. Detritivores
Sea cucumbers are primarily detritivores, meaning they feed on organic matter and detritus present in the sediments and on the seabed. They ingest dead plants, algae, and small animals, helping to decompose and recycle organic material. This process is vital for nutrient cycling in marine ecosystems.
2. Bioturbation
As sea cucumbers move through the sediments, they actively disturb and churn the substrate. This bioturbation process enhances sediment aeration and promotes the mixing of organic material, minerals, and nutrients. This can increase the availability of nutrients to other benthic organisms and influence sediment structure.
3. Nutrient Cycling
Sea cucumbers help release nutrients (such as nitrogen and phosphorus) locked in organic matter, making these nutrients available to other organisms in the ecosystem. This nutrient cycling supports primary producers like phytoplankton and macroalgae, which form the basis of marine food webs.
Read also: Get To Know About 10 Fun Facts of Lobster
4. Sediment Stabilization
Sea cucumbers can stabilize sediments by burrowing into the substrate. This behavior helps prevent erosion and sediment resuspension during wave action and strong currents, contributing to the overall stability of coastal ecosystems.
5. Habitat for Other Species
The burrows and crevices created by sea cucumbers provide shelter and refuge for a variety of small marine organisms, including polychaete worms, small fish, and crustaceans. These habitats enhance biodiversity and create microenvironments within the sediments.
6. Predation and Trophic Interactions
Sea cucumbers serve as a food source for various predators, including sea stars, fish, and some crustaceans. Their presence in the food web supports the populations of these predators and contributes to trophic interactions in marine ecosystems.
Read also: Exploring the Variety of Seafood Dishes from Indonesia
7. Biological Filter Feeding
Some sea cucumber species are filter feeders, capturing suspended particles from the water column. While not all sea cucumbers exhibit this behavior, filter-feeding species can influence water clarity and nutrient levels in their local environment.
8. Ecosystem Resilience
By participating in nutrient cycling and sediment stabilization, sea cucumbers contribute to the overall resilience of marine ecosystems. Their activities help maintain stable and productive habitats for a wide range of species.
9. Indicator Species
Changes in sea cucumber populations and behavior can serve as indicators of environmental conditions and ecosystem health. Monitoring sea cucumbers can help scientists assess the impacts of environmental disturbances and pollution.
In summary, sea cucumbers play vital ecological roles in marine ecosystems by contributing to nutrient cycling, sediment stability, habitat provision, and biodiversity support. Their activities have far-reaching effects on the health and functioning of coastal and benthic ecosystems, highlighting their importance in maintaining the balance of these environments.
Read also: Expert Tips for Fresh and Flavorful Lobster
.jpg)
The Impact of HACCP-Based Integrated Quality Management Programs on the Quality and Competitiveness of Fresh Demersal Fish Products
 and Employee Productivity on the Demersal Fish Processing Floor.jpg)

.jpg)