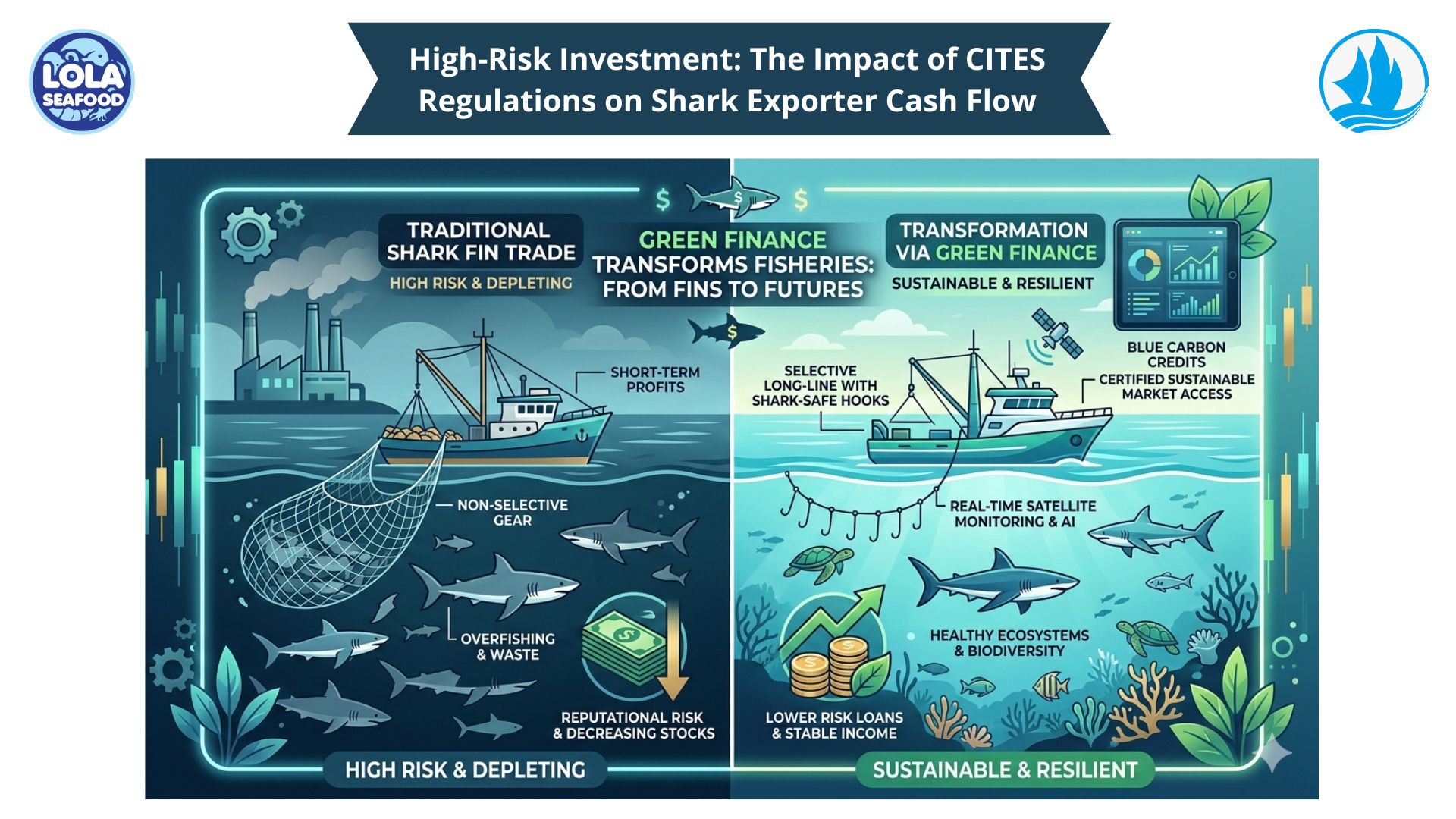
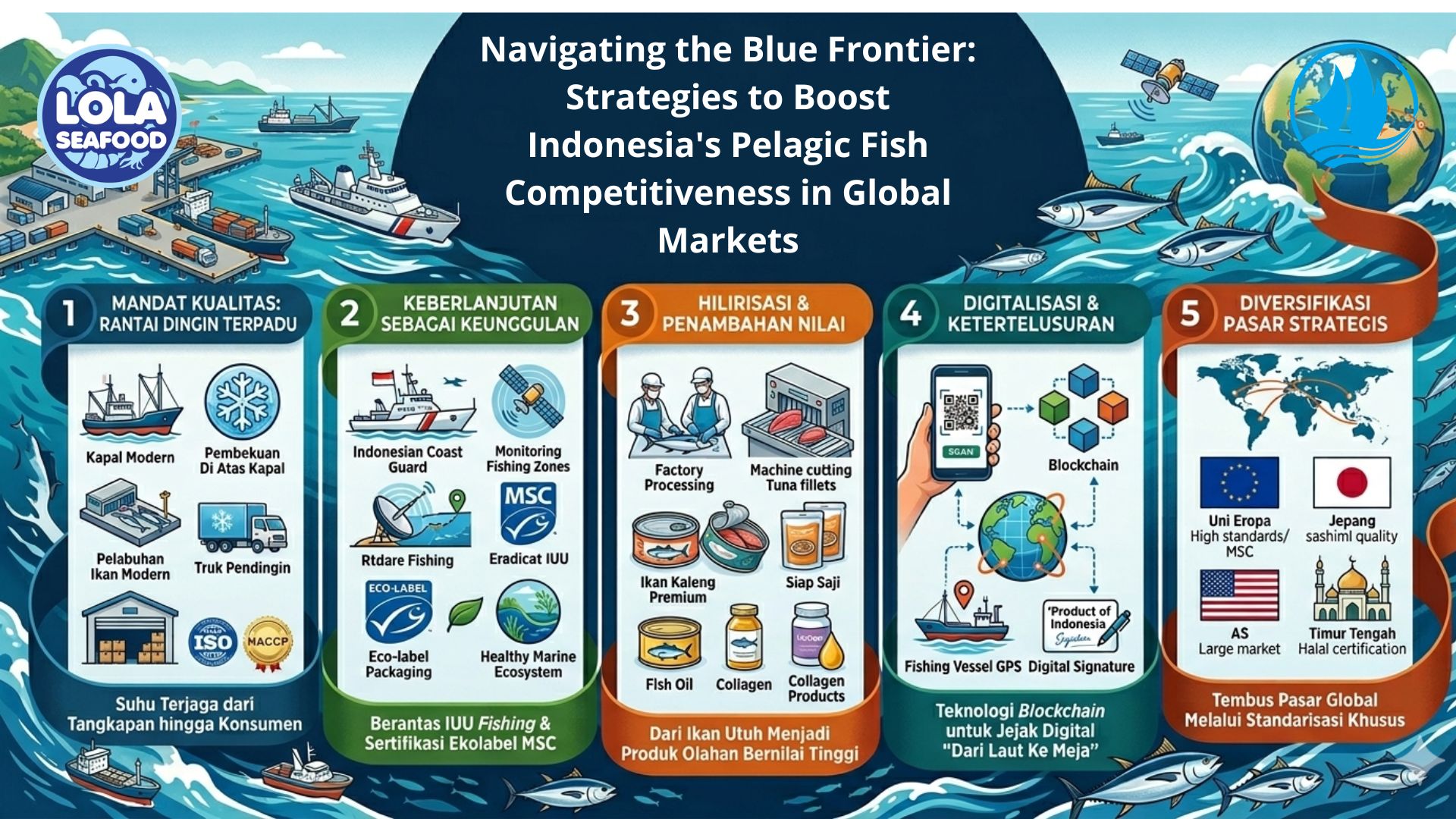
Total Plate Count (TPC)
By. Najih - 04 Sep 2024
Total Plate Count (TPC) is a count of microbial load in a sample i.e. it an enumeration of all heterotrophic bacteria that will grow in aerobic or microaerophilic conditions that will grow at 350C. This plate count will tell you how good your sanitization plan is, measure the safety of your product or water supply. This test is the most common test done in factories. It is measured in CFU or colony forming units based on the premise that a bacteria which is invisible to the naked eye will grow to form a cluster or colony which then becomes visible, when in contact with appropriate nutrients and temperature and it is properly spread out. The other counting method often used is a statistical method called MPN method. Here counting is based on viable colonies which can grow in a liquid medium contained in a series of 3 or 5 or even 10 tubes in different concentration. The number of positive tubes is referred to a chart which will give you the most probable number of bacteria in your sample.
Film Method - Compact Dry TC
R-Biopharm Indonesia supplies the Compact Dry TC. Compact Dry TC contains a standard nutrient medium for detection of total plate count. Due to the tetrazolium salt which is integrated into the medium and serves as redox indicator die, the grown colonies will be red coloured and therefore easily to identify and differentiable from possible food residues on the plate.
Conventional Method - Biolife Italiana
Total plate count can be made using plate count agar. This microbiological growth medium is not a selective medium, Arasains Indonesia provides Biolife Standard plate count agar. Typically, this agar consists of peptone, yeast extract glucose and agar. Two methods of growing are usually practiced- the pour plate or the spread plate. The pour plate mixes the sample and the agar at 45°C and pours it onto a petri dish. The spread plate method uses a solidified agar plate and uses a spreader to spread the bacteria onto the plate.