Thawing Frozen Fish by Air Circulation
By. Nugroho Luhur - 03 Jan 2025.jpg)
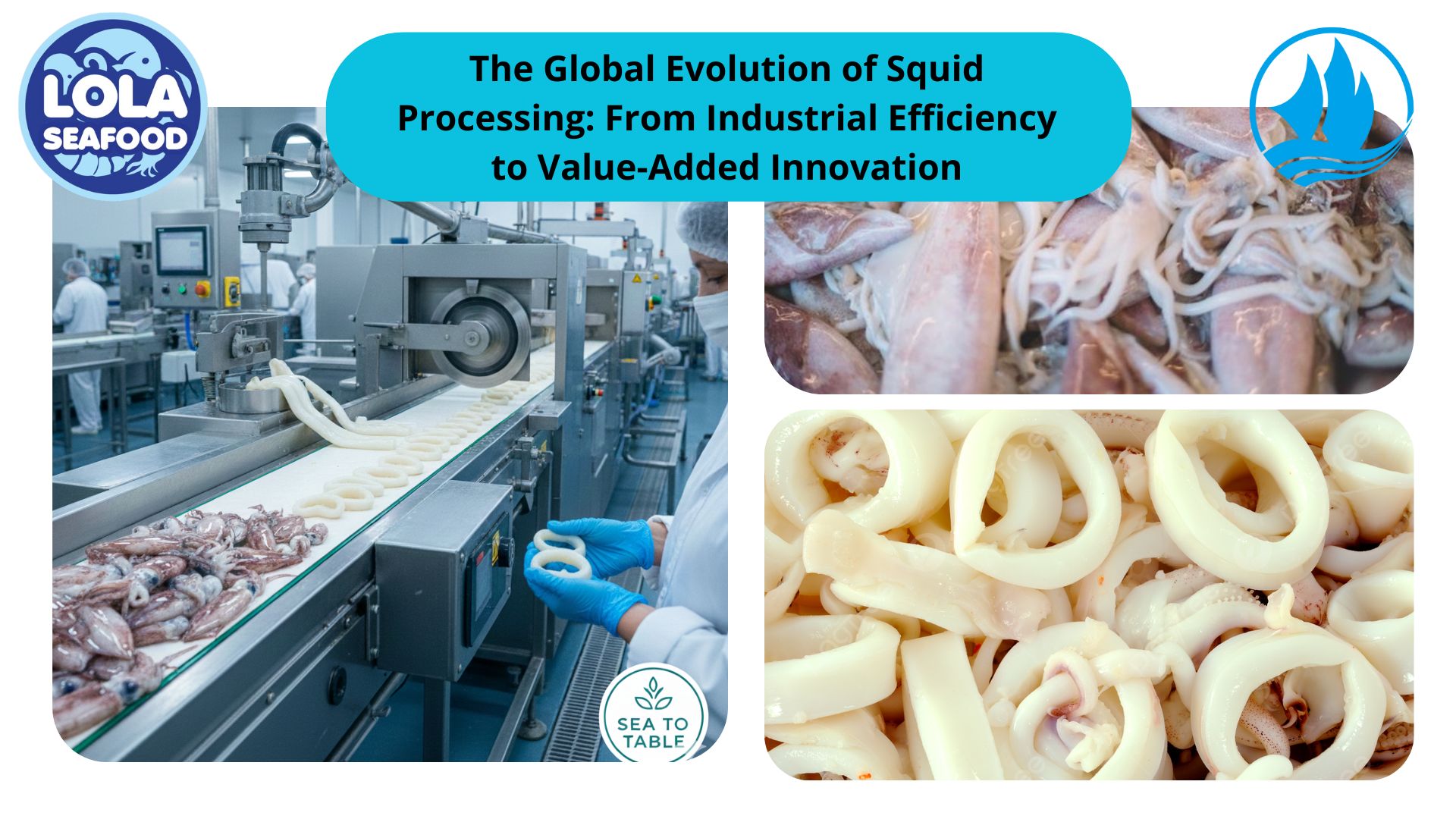
Kelolalaut.com Thawing frozen fish using air circulation is a widely used method in the seafood industry and home kitchens due to its simplicity and efficiency. Proper thawing is critical to maintaining the quality, texture, and safety of fish. This method relies on the controlled movement of air around the frozen product to gradually raise its temperature and allow the ice crystals within the fish to melt without compromising its integrity.
How the Process Works
The air circulation method involves placing frozen fish in an environment where air is moved around it at a specific temperature and humidity level. The airflow ensures that the fish thaws evenly, preventing areas from being overexposed to heat or moisture. The process typically follows these steps:
- Preparation:
- Remove the fish from its original packaging, especially if it is vacuum-sealed, to allow proper airflow.
- Place the fish on a wire rack or perforated surface to ensure that air can circulate around all sides.
- Controlled Environment:
- The thawing process requires a controlled environment with temperatures between 0°C (32°F) and 4°C (39°F). This ensures that the fish remains out of the "danger zone" (4°C to 60°C or 40°F to 140°F), where bacteria can multiply rapidly.
- Air circulation is typically achieved using fans or specialized thawing equipment.
- Airflow and Humidity:
- Continuous air circulation prevents the formation of hot or cold spots, ensuring even thawing.
- Maintaining optimal humidity levels (around 70%–90%) prevents the fish from drying out or becoming overly moist, preserving its texture and appearance.
- Monitoring:
- Regular checks on the temperature of the fish and the thawing environment are crucial to prevent partial cooking or spoilage.
- Most fish thaws completely within 6 to 12 hours, depending on size and thickness.
Advantages of Air Circulation Thawing
- Even Thawing: The consistent airflow ensures that the fish thaws uniformly, reducing the risk of partially thawed areas that could lead to uneven cooking or bacterial growth.
- Preservation of Quality: This method prevents the fish from sitting in water (as it might in water-based thawing methods), which could leach out nutrients and alter texture.
- Reduced Risk of Bacterial Growth: By keeping the thawing temperature below 4°C, the method minimizes the chance of bacteria proliferating on the surface of the fish.
- Scalability: Air circulation thawing can be applied to small batches of fish in a home kitchen or large quantities in industrial settings using specialized equipment.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
- Time Consumption: Air circulation thawing takes longer than some other methods, such as water immersion. However, the extended time ensures better quality and safety.
Solution: Plan ahead to allocate sufficient time for thawing. For urgent needs, a combination of air circulation and slightly higher temperatures (still within safe limits) can speed up the process.
- Energy Consumption: Continuous air circulation requires electricity, especially in industrial settings.
Solution: Use energy-efficient fans or equipment and ensure the system is well-insulated to minimize energy loss.
- Moisture Loss: If humidity levels are not properly controlled, the fish may lose moisture, resulting in a dry texture.
Solution: Use humidifiers or place a shallow pan of water near the fish to maintain optimal humidity.
Applications in Industry and Home Settings
-
- Industrial Use: Large-scale seafood processing facilities often employ specialized thawing chambers with controlled air circulation to handle bulk quantities. These chambers are equipped with automated systems to monitor temperature, humidity, and airflow.
- Home Use: For home kitchens, thawing fish in the refrigerator with air circulation is a practical approach. Placing the fish on a wire rack in the refrigerator allows for safe and gradual thawing.
Best Practices for Air Circulation Thawing
-
- Always clean and sanitize the thawing area to prevent cross-contamination.
- Avoid refreezing fish after it has thawed, as this can degrade its quality.
- Use a thermometer to check the internal temperature of the fish to ensure it remains within safe limits.
In conclusion, thawing frozen fish by air circulation is a reliable method that balances efficiency, quality preservation, and food safety. Whether for industrial applications or home use, following best practices ensures the fish retains its natural flavour, texture, and nutritional value. By understanding and applying the principles of air circulation thawing, seafood enthusiasts can enjoy their meals at their finest quality.
If youre interested in our Emperor Fillet Skinless, Snapper Fillet Skinless, Crimson Snapper Whole Round, Parrotfish Fillet Skinless, and Grouper Fillet Skinless please do not hesitate to contact us through email and/or whatsapp
.jpg)
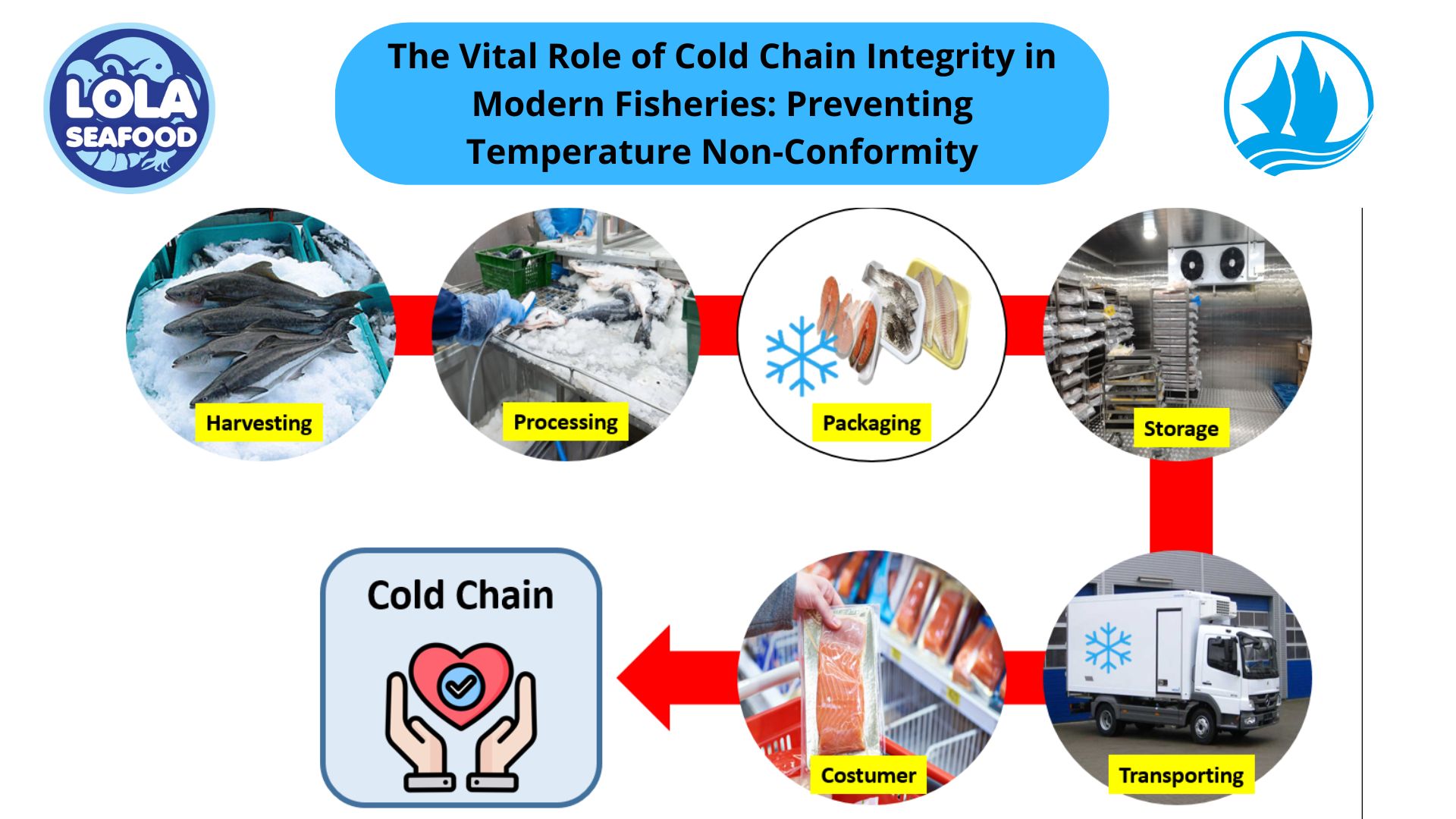
The Impact of HACCP-Based Integrated Quality Management Programs on the Quality and Competitiveness of Fresh Demersal Fish Products
 and Employee Productivity on the Demersal Fish Processing Floor.jpg)

.jpg)