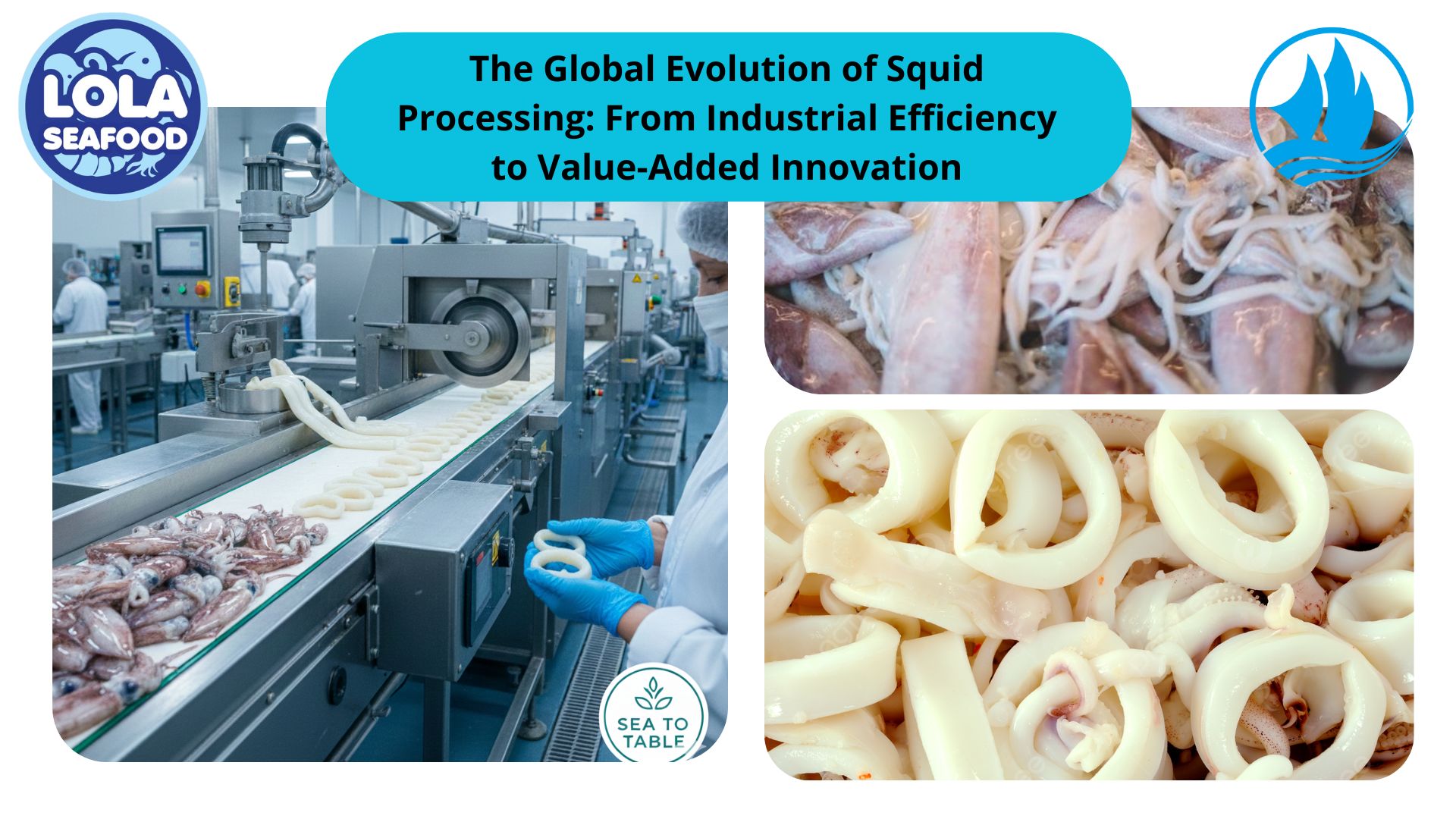
This Is The Understanding of Public Finance
By. Lutfi - 22 Jan 2025 (1).png)
kelolalaut.com Definition of Public Finance
Public finance is a branch of economics that studies how governments manage revenues and expenditures to achieve public welfare. It encompasses the analysis of how income is obtained through taxes, budget management, debt financing, and resource allocation for public needs. Public finance plays a vital role in ensuring economic stability, equitable income distribution, and the provision of public goods and services that cannot be efficiently supplied by the private sector.
Objectives of Public Finance
Public finance has several primary objectives, including:
- Improving Public Welfare
Governments use public finance to provide basic services such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and security, thereby enhancing the quality of life for citizens.
- Economic Stability
By regulating government spending and income, public finance helps maintain economic stability, prevent inflation or deflation, and reduce the impact of recessions.
- Income Redistribution
Progressive taxation and social programs are designed to reduce disparities between the rich and the poor.
- Provision of Public Goods and Services
Certain goods and services, such as roads and defense, cannot be efficiently provided by the private sector due to their non-rival and non-exclusive nature.
Components of Public Finance
Public finance consists of several key components:
- Government Revenue :
- Taxes : The main source of government income, including income tax, value-added tax (VAT), and customs duties.
- Non-Tax Revenue: Income from fines, dividends from state-owned enterprises, and natural resources.
- Government Expenditure :
- Productive Expenditure: Investments in infrastructure, education, and healthcare.
- Non-Productive Expenditure: Debt payments and subsidies.
- Public Debt :
- Governments may borrow domestically or internationally to finance budget deficits.
- Government Budget : The budget reflects the government's financial plan for a specific fiscal year, including revenue and expenditure estimates.
- Fiscal Stability : Governments use fiscal policies, such as changes in taxes and spending, to maintain a balance between income and expenditure.
Challenges in Public Finance
- Budget Deficit : When government spending exceeds revenue, it can lead to excessive debt.
- Efficient Allocation : Governments must ensure resources are allocated efficiently to maximize their impact on society.
- Tax Compliance : Low levels of tax compliance can reduce state revenue and limit the government’s ability to provide public services.
- Corruption : Poor transparency in management can harm the public and hinder economic growth.
Conclusion
Public finance is a crucial element in economic development and public welfare. With proper management, governments can create an environment conducive to economic growth, reduce inequality, and improve citizens’ quality of life. However, achieving these goals requires transparent, accountable, and public-oriented policies.
If you are interested in our baby octopus flower, baby octopus whole cleaned and baby octopus whole round please do not hesitate to contact us through email and/or whatsapp

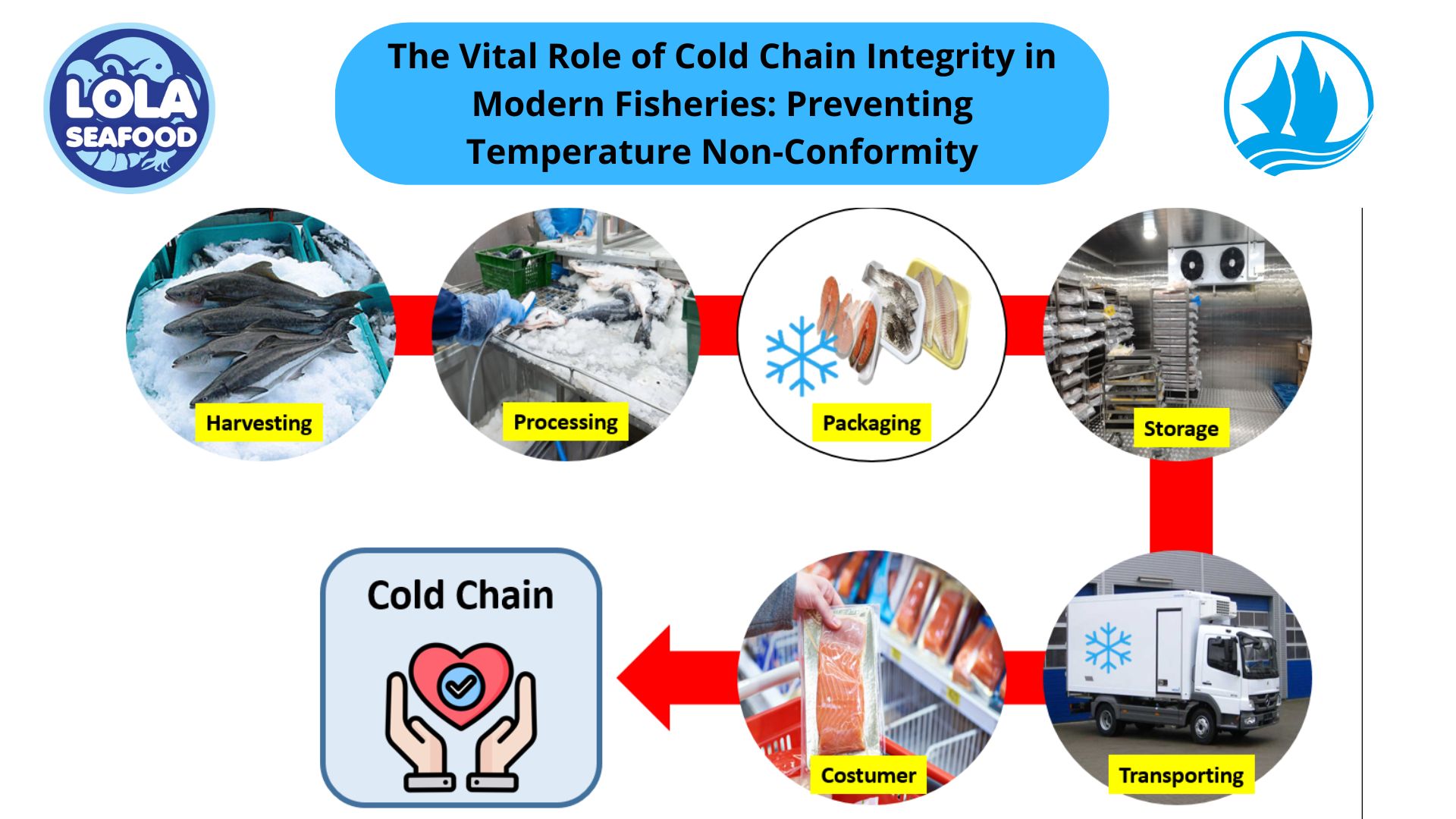
Mitigating Biological and Chemical Hazards: Our Rigorous 7-Step HACCP Protocol in Wild-Caught Fisheries

.jpg)



.jpg)