SALMON NUTRIENTS
By. Najih - 27 Mar 2024
Salmon is undeniably delicious. It has a unique, delicate flavour with a less “fishy” taste than many other varieties of fatty fish, such as sardines and mackerel.
It is also extremely versatile. It can be steamed, sauteed, smoked, grilled, baked, or poached. It can also be served raw in sushi and sashimi.
Consuming salmon can help protect against heart disease by increasing levels of omega-3 fats, decreasing levels of omega-6 fats, and lowering triglycerides.
Consuming salmon may help you manage your weight by reducing your appetite, temporarily boosting your metabolism, and decreasing belly fat.
Salmon and other fatty fish can help lower inflammation, which may reduce risk factors for several diseases and improve symptoms in people with inflammatory conditions.
Frequent salmon consumption may help protect fetal brain health in pregnancy, preserve brain function, and decrease the risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
Some studies have found that eating fish or increasing your intake of omega-3 fatty acids could reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety and improve mood.
Salmon contains nutrients like astaxanthin, vitamin A, and omega-3 fatty acids, all of which could help promote eye health.
Salmon is rich in vitamin D and phosphorus, which can support bone health. Some studies show that eating fish could be linked to a lower risk of osteoporosis, but more research is needed.
Here is a closer look at the nutritional value for a 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving of cooked wild or farmed salmon
Wild salmon Farmed salmon
Calories 182 206
Protein 25 grams 22 grams
Fat 8 grams 12 grams
Vitamin B12 127% of the Daily Value (DV) 117% of the DV
Vitamin B6 56% of the DV 38% of the DV
Selenium 85% of the DV 75% of the DV
Niacin 63% of the DV 50% of the DV
Pantothenic acid 38% of the DV 30% of the DV
Thiamine 23% of the DV 28% of the DV
Phosphorus 21% of the DV 20% of the DV
.jpg)




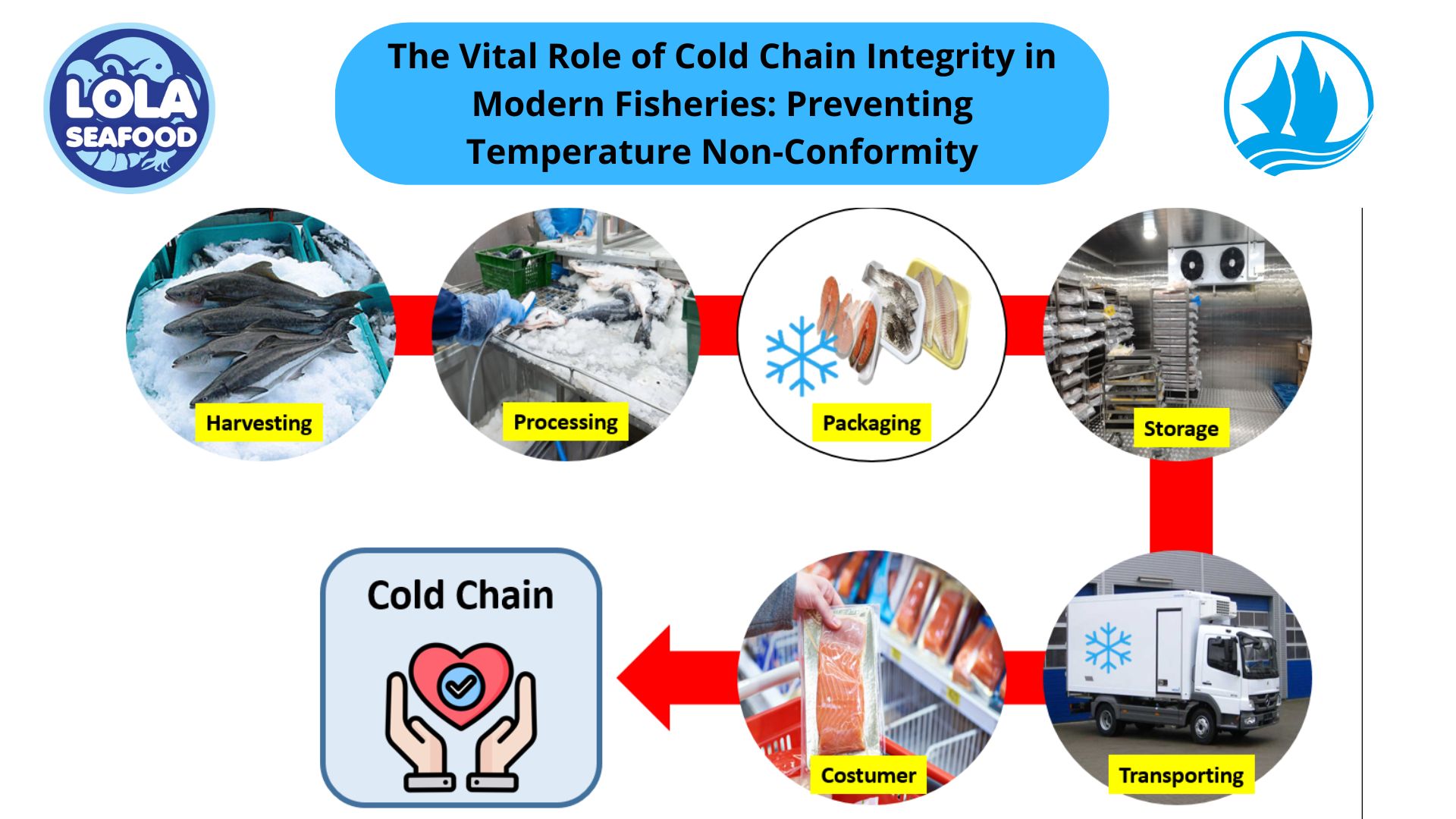
.jpg)
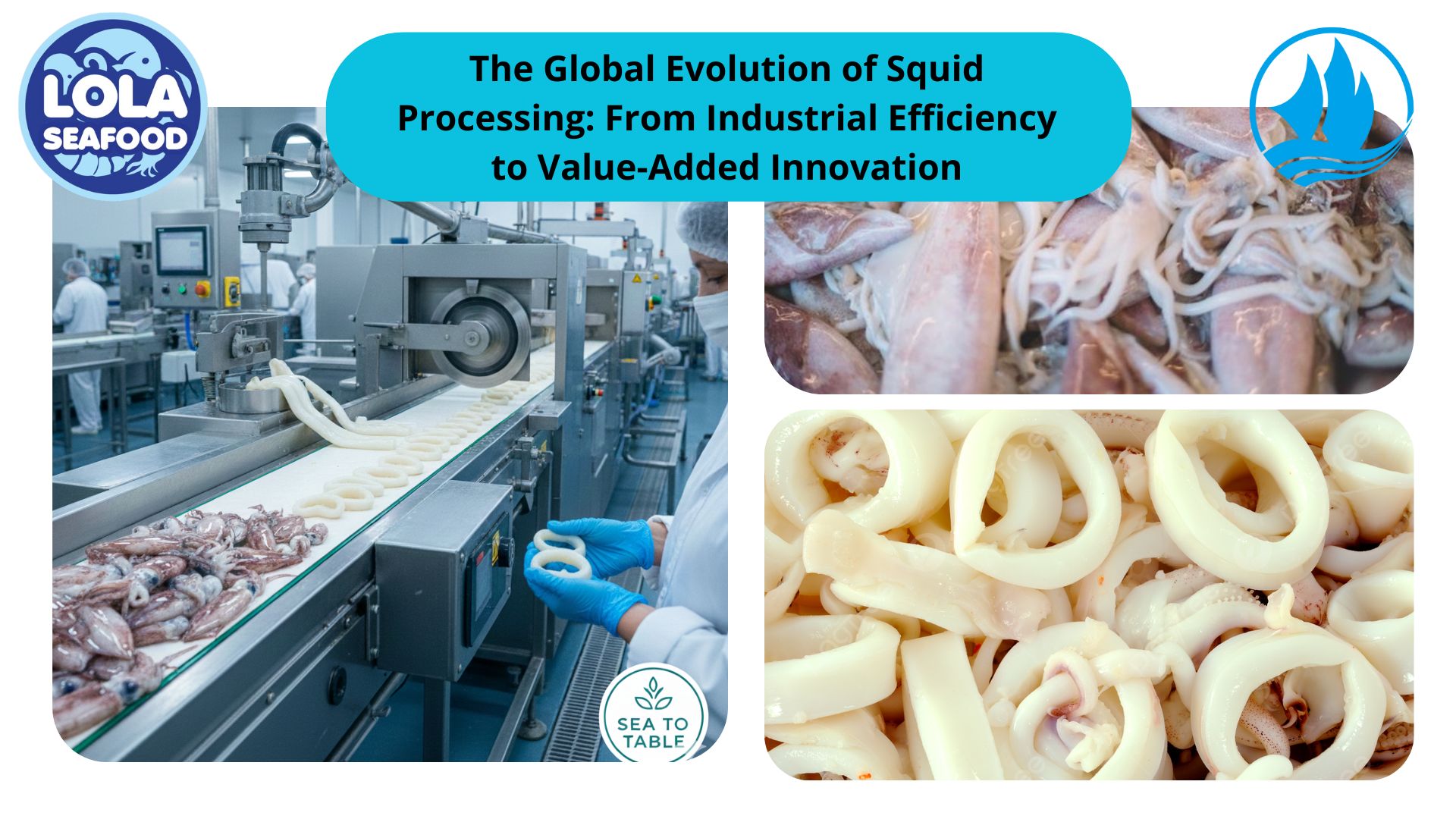
.jpg)