Understanding the Processing Stages of Pelagic Fish
By. Najih - 12 Sep 2024.jpg)
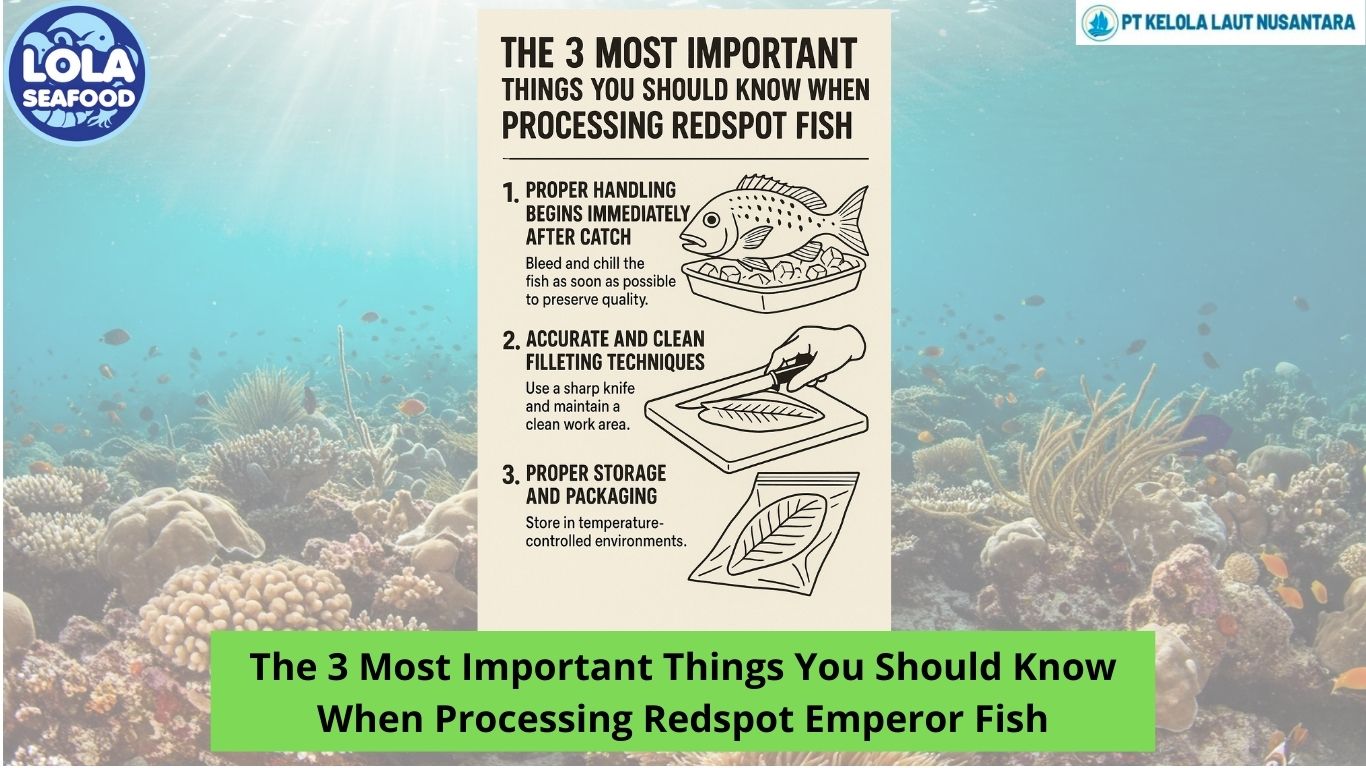
Processing demersal fish, such as cod, haddock, and flatfish, involves several critical stages to ensure that the fish remains fresh and of high quality. This article outlines these essential stages, providing insights into how each step contributes to maintaining the integrity of the final product.
1. Catching and Immediate Handling
The processing journey begins with the catch. Immediate handling is crucial for preserving the quality of demersal fish. Fishermen use methods designed to minimize stress and damage, such as employing suitable nets and quickly chilling the fish. Once onboard, the fish are rapidly cooled with ice or refrigerated water to slow down metabolic processes and prevent spoilage.
2. Sorting and Grading
After initial handling, the fish undergo sorting and grading. Sorting involves separating fish based on species, size, and quality, ensuring that only the best specimens move forward in the processing chain. Fish not meeting quality standards are either discarded or used for other purposes. Grading helps determine the appropriate processing methods and pricing, ensuring that each fish is handled according to its market value.
3. Cleaning and Evisceration
Cleaning and evisceration are vital for preventing contamination and ensuring a longer shelf life. During this stage, internal organs and blood are removed. Proper cleaning removes contaminants, while evisceration eliminates organs that could lead to spoilage if left inside. This step is essential for maintaining both the quality and safety of the fish.
4. Filleting and Portioning
Once cleaned, the fish are filleted and portioned. Filleting involves removing bones and skin to produce boneless, skinless fillets. Precision in this step is key to maximizing yield and minimizing waste. The fillets are then portioned into sizes suitable for various market segments, such as retail or food service.
5. Freezing and Storage
To maintain freshness, demersal fish are often frozen shortly after processing. Freezing halts bacterial growth and preserves texture and flavor. Blast freezing is typically used to ensure even freezing, which helps in retaining high quality. Proper storage conditions are critical to prevent freezer burn and maintain product integrity.
6. Packaging and Distribution
The final stage involves packaging and distribution. Fish fillets are packed in vacuum-sealed bags or other suitable materials to prevent contamination. Efficient distribution ensures that the fish reaches the market in optimal condition, maintaining the cold chain throughout.

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)