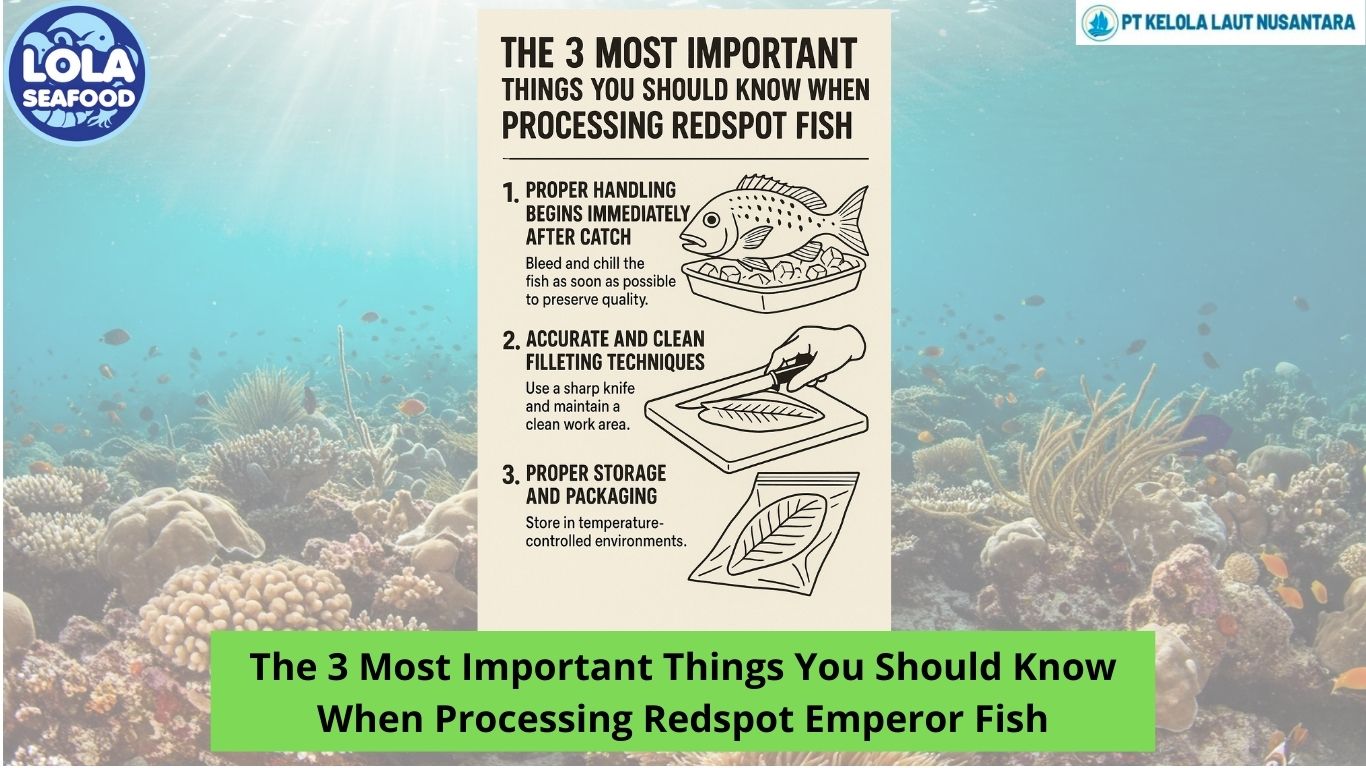
Here are The Depreciation: Definition, Types, Factors, Methods, and Examples
By. Lutfi - 31 Jan 2025 (1) (1).png)
kelolalaut.com 1. Definition of Depreciation
Depreciation is the process of allocating the cost of fixed assets over their useful life due to usage, wear and tear, or other economic factors. Depreciation is recorded in financial statements to reflect the asset’s decline in value over time. Depreciation is important in accounting because it helps companies allocate asset costs systematically and provides a more accurate picture of the asset's value in financial statements.
- Causes of Depreciation
Depreciation can occur due to several factors, such as:
• Usage : The asset is used continuously in business operations.
• Obsolescence : The asset becomes outdated due to technological advancements.
• Economic Factors : Changes in economic conditions cause the asset to lose value.
• Environmental Factors : The asset experiences damage due to weather, corrosion, or other environmental factors.
- Types of Depreciation
Depreciation can be categorized into several types, such as:
- Physical Depreciation
Occurs due to the usage of the asset in business operations or environmental factors like weather and corrosion. For example, a factory machine that wears out due to continuous use.
- Functional Depreciation
Occurs because the asset is no longer efficient or suitable for the needs, even though it can still be used. For example, an old computer that still works but doesn’t support the latest software.
- Economic Depreciation
Occurs due to changes in economic conditions or technology, causing the asset to lose value before its useful life ends. For example, a production machine whose value decreases due to the emergence of more advanced technology.
- Factors Affecting Depreciation
Several factors affect the amount of depreciation of an asset, including:
• Acquisition Cost : The initial cost spent on purchasing the asset.
• Residual Value : The estimated value of the asset at the end of its useful life.
• Useful Life : The period during which the asset can be used before it becomes unproductive.
• Usage Intensity : The more frequently the asset is used, the faster it depreciates.
- Depreciation Methods:
- Straight-Line Method
This is the simplest and most commonly used depreciation method. The depreciation expense is calculated evenly each year over the asset's useful life.
-
- Declining Balance Method
This method results in higher depreciation expenses in the earlier years, decreasing in the subsequent years. It is typically used for assets that depreciate quickly, such as vehicles or electronics.
-
- Sum of the Years’ Digits Method (SYD)
This method also results in higher depreciation expenses at the beginning but uses a calculation based on the sum of the years’ digits.
-
- Units of Production Method
This method calculates depreciation based on the number of units produced or hours worked by the asset.
Conclusion
Each depreciation method has its advantages and disadvantages. Companies must choose the method that best suits the type of asset and their business model to ensure more accurate financial reporting that reflects the true condition of the asset.
Commonly used methods:
• Straight-line for assets used consistently.
• Declining balance for assets that quickly lose value.
• Units of production for assets dependent on output levels.
If you are interested in our Black Pomfret Portion Cut and Black Pomfret Whole Round please do not hesitate to contact us through email and/or whatsapp.